
Have you ever wondered what it would be like to turn your digital creations into tangible objects? To witness the transformation of mere pixels into solid plastic, bringing your imagination to life? Welcome to the enchanting world of 3D printing, where technology and creativity collide to unlock a realm of endless possibilities. In this article, we will embark on a captivating journey to uncover the magic behind 3D printing technology. We will delve into its inner workings, explore the wonders of plastic 3D printing, unravel the origin of the plastic used. So, fasten your seatbelts and let the journey begin!
What is 3D printing?
Imagine a process that allows you to materialize your wildest dreams. 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, does exactly that. It empowers you to transform your digital designs into three-dimensional physical objects. It's as if you possess the power to breathe life into your imagination, effortlessly transcending the boundaries of traditional manufacturing methods.
How does 3D printing work?
The journey from pixels to plastic begins with a digital 3D model created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The model is then sliced into thin layers, which serve as a blueprint for the printer. Each layer is printed individually, often using melted thermoplastics or photopolymer resins, until the complete object is formed.
From Pixels to Plastic: The Process Unveiled
Designing the 3D model

The journey of a 3D printed object starts with a creative spark and a digital design. Skilled designers and engineers utilize CAD software to craft intricate models, leveraging their expertise to bring ideas to life. This step involves meticulous planning, attention to detail, and an understanding of the printer's capabilities and limitations.
Selecting the appropriate printing material

Choosing the right printing material is crucial for achieving the desired characteristics and functionality of the printed object. From flexible and durable plastics to metal alloys and biocompatible resins, the range of available materials continues to expand, catering to a wide array of applications.
Printing the model layer by layer

With the design prepared and the printer calibrated, it's time to embark on the printing journey. The printer's nozzle or laser follows the instructions from the slicing software, depositing or solidifying the printing material layer by layer. This iterative process continues until the object is fully realized, with complex geometries and intricate details faithfully reproduced.
The role of slicing software
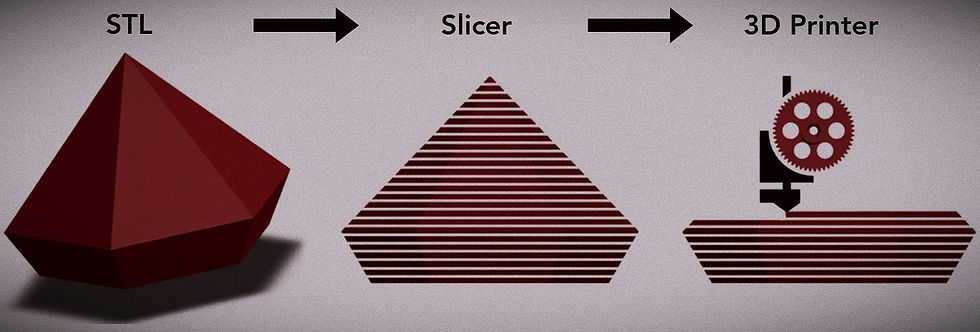
Slicing software acts as the bridge between the digital model and the physical print. It takes the 3D model and slices it into thin layers, generating the necessary instructions for the printer. This software allows users to adjust settings like layer height, print speed, and infill density, influencing the final print quality and time.
Post-processing and finishing touches

Once the printing is complete, the object may undergo post-processing to enhance its appearance or functionality. This may involve removing support structures, sanding rough edges, applying surface treatments, or even combining multiple printed parts into a seamless whole. The level of post-processing required depends on the intended use and desired finish of the object.
What Materials are Used in 3D Printing?
Plastics are among the most commonly used materials in 3D printing, with filaments such as PLA (polylactic acid) and ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) being popular choices. Additionally, there are specialized filaments available, such as PETG (polyethylene terephthalate glycol), TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane), and nylon, which offer specific characteristics like flexibility, strength, or chemical resistance. Beyond plastics, metals like titanium, aluminum, and stainless steel can be utilized in metal 3D printing processes such as selective laser melting (SLM) or direct metal laser sintering (DMLS).
What Can I Make with a 3D Printer?
Now, let's address the main question at hand: what can you make with a 3D printer? The possibilities are truly boundless. From practical items like phone cases, kitchen gadgets, and customized jewelry to more complex creations like mechanical parts and architectural models, a 3D printer opens a realm of opportunities. Want to express your artistic side? Create sculptures, figurines, or intricate home decor pieces. Need a spare part for your broken household item? 3D print it. Whether you are a hobbyist, a professional, or simply curious, a 3D printer invites you to unleash your creativity.
But the magic of 3D printing extends far beyond personal creativity. It has the power to revolutionize industries, opening up new avenues of innovation and progress. In healthcare, it can create prosthetics tailored to individual needs, improving the quality of life for those in need. In the automotive and aerospace sectors, it enables the production of lightweight components that enhance performance and fuel efficiency. Even in architecture and construction, 3D printing pushes the boundaries of what can be built, unleashing the imagination of architects and designers.
From pixels to plastic, 3D printing has transformed the way we create, design, and manufacture objects. Imagine holding in your hands a creation that was once just a figment of your imagination. The emotions that surge through you as you run your fingers over the intricate details and marvel at the precision and craftsmanship are indescribable. It's a sense of pride and accomplishment, knowing that you have the power to bring your visions to life. So, embrace the magic of 3D printing and let your imagination soar.

Komentar